Front of Pack Nutrition Labelling FAQs – FSSAI Regulation
October 26, 2022

Q1. What is the meaning of Front of the pack?
“Front of the pack” means part of the package that faces forward (in the principal field of vision) and is typically the first thing a consumer will see when they look at the product.”
Q2. What is FoPNL in India?
The full form of FoPNL is Front of Pack Nutrition Labeling. Front-of-pack nutrition labelling (FOPNL) is a form of supplementary nutrition information that presents simplified nutrition information on the front-of-pack of pre-packaged foods. It can include symbols/graphics, text or a combination thereof that provide information on the overall nutritional value of the food and/or on nutrients included in the FoPNL.
Q3. What does HFSS food mean?
High fat, sugar, salt (HFSS) food means a processed food product that has high levels of saturated fat or total sugar or sodium. The declared values of these ingredients are such that the product; does not satisfy the value of energy (kcal) from total sugar less than 10 percent of total energy, or from saturated fat 10 percent of total energy, and sodium less than 1 mg/1 kcal.
Q4. What is the threshold for a food to be called high sugar or high fat or high in sodium?
A product is considered high in sugar/ fat if the energy (kcal) from total sugar or saturated fat is more than 10 percent of total energy and a product is considered high in sodium if it contains sodium more than 1 mg/1 kcal of food.
Q5. What is INR?
Indian Nutrition Rating (INR) is the system of pictorial display of the nutritional quality of the food on the front of the pack.
Q6. What are the health risk-increasing factors that are included in calculating food ratings for FoPNL?
The four health risk-increasing factors are energy, total sugars, saturated fat and sodium per 100g or per 100ml of the product.
Q7. What are the Positive Nutrients that are considered in calculating food ratings for FoPNL?
Positive nutrients viz., fruit & vegetable (FV); nuts, legumes & millet (NLM); fiber and protein will be considered in calculating the food rating of specific solid foods or liquid foods.
Q8. What are the categories of food included- foods are classified into Solid, liquid and exempt
All processed and packaged food products covered under the extant FSS Regulations are classified into three categories viz., CATEGORY-I (Solid foods), CATEGORY-II (Liquid foods) and CATEGORY-III (Exempted from FOPNL).
Q9. What are the food products that are exempted?
The food products that are exempted from FOPNL under INR are milk and milk products, Oils and Fats, fruits & vegetables, grains and flours, pulses & legumes, eggs, fish, poultry & Meat, sugars and spices, alcohol and beverages.
A detailed list of food products that are exempted from FOPNL can be found under Category III in schedule IV.
Q10. How does the INR system rate the overall food nutritional profile for packaged food?
INR system rates the overall nutritional profile for packaged food by assigning it a rating from ½ star (least healthy) to 5 stars (healthiest). More stars indicate that the food product is better positioned to provide for the daily human need for nutrients.
Q11. What is the formula that will be used to calculate the INR for the front-of-the-pack labelling?
Final INR Score = (INR baseline points) – [(INR FV* points) + (INR NLM* points) + (INR P* points) + (INR F* points)]
Q12. What components make baseline points?
Baseline points are calculated using 4 health risk-increasing factors – energy, total sugars, saturated fat, and sodium for solid foods per 100g product, and using energy and total sugars for liquid foods per 100ml product on an “as sold” basis.
Q13. What is the baseline reference value for food risk factors?
The baseline reference value for food risk factors per 100g/ 100ml- Energy: 400kcal, Total sugar: 21g, Saturated fat: 5g, Sodium: 450mg.
Q14. What are FV, NLM, P & F points?
FVNLM points are the points calculated using the percentage of fruits, vegetables, nuts, legumes, and millet. For Liquid foods only, FV points are to be considered and not NLM points.
Q15. How are P & F points calculated?
Protein and fiber points are calculated using protein and fiber amounts. For liquid foods, only protein points are to be considered and not fiber points.
Q16. What is the format of the logo for INR?
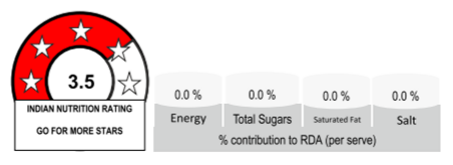
The format of the logo should be as shown below.
Q17. Where should the logo be displayed?
The logo shall be displayed close in proximity to the name or brand name of the product on the front of the pack.
Q18. Is it mandatory for FBOs to have the INR?
Yes, the compliance shall be voluntary until a period of 48 months from the date of final notification of these regulations and mandatory thereafter.
Q19. Is it mandatory for the operators to provide additional information declaring per serve % contribution to RDA of energy, sugars, SFAs and sodium?
No, it is optional for food business operators to provide additional interpretive information as per serve percentage contribution to RDA of energy, total sugars, saturated fats and sodium expressed as salt equivalent, along with the INR logo.
Q20. What are the regulated dimensions of the logo?
SR. NO | Area of the principal display panel in cm. sq. | Minimum Height (mm) | Minimum Width (mm) |
1. | Above 100 to 500 | 15 | 15 |
2. | Above 500 to 2500 | 20 | 20 |
3 | Above 2500 | 25 | 25 |
The dimensions of the logo should be as given in the table respective to the area of the principal display panel.

Zahra Merchant (M.Sc. Food Processing & Preservation)
Zahra is very communicative, detail oriented and a team player. She is very proud of having the ability to multitask and manage time efficiently.
